Monolithic applications carry a familiar weight: slow to adapt, tricky to scale, and all too eager to break under pressure. Code changes drag, deployments demand caution, and integration points become fragile chokeholds. For many organisations, the result is slower innovation and mounting technical debt—but modern cloud architectures are shifting that story.
Cloud-based microservices have been gaining popularity in recent years as a more flexible and scalable alternative to traditional monolithic architectures. And when it comes to deploying microservices, Amazon Web Services (AWS) has emerged as the go-to platform.
In this insight, we'll explore the world of microservices on AWS, arming you with the knowledge and tools to tame even the unruliest of applications. By the end, you'll be ready to break free from the monolithic shackles and embrace a brighter, more modular future.

Understanding Microservices Architecture
Before we dive into the specifics of AWS implementation, let's take a moment to understand what microservices are and why they've become so popular. At its core, a microservices approach is all about breaking down a large, complex application into smaller, more manageable services. Each service is responsible for a specific business capability and can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently, bringing a number of benefits:

- Scalability: Services can be scaled up or down independently based on demand
- Flexibility: New features can be added to individual services without affecting the entire application
- Independent deployments: Services can be updated and deployed separately, reducing the risk and impact of failures
At the same time, unsurprisingly, microservices do come with their own set of challenges:
- Increased complexity: Managing multiple services can be more complex than a single monolithic application
- Potential performance issues: Communication between services can add latency and overhead
With the right tools and practices, however, these challenges can be overcome — and that's where AWS comes in!
AWS Tools and Services for Microservices
AWS offers a wide range of services and tools specifically designed to support microservices architectures. Let's take a look at some of the key players:
- Amazon EC2
: Provides resizable compute capacity, allowing you to run your microservices on virtual servers.
- Amazon ECS
and Amazon EKS
: Make it easy to deploy, manage, and scale your containerized microservices.
- AWS Lambda
: Lets you run code without provisioning or managing servers, perfect for building serverless microservices.
- Amazon API Gateway
: Acts as the front door for your microservices, handling API management, authentication, and traffic control.

With so many options, how do you choose the right tools for your needs? The key is to consider your specific requirements and constraints. Do you need the flexibility and control of running your own containers on EC2, or would a managed service like ECS or EKS be a better fit? Is serverless the way to go for your use case, or do you need the power and customization of a traditional server?
There's no one-size-fits-all answer, but with a little careful consideration (and perhaps a coin toss or two), you'll be well on your way. Let's take a closer look at some best practices for designing and deploying your microservices on AWS.
Designing Cloud-based Microservices on AWS
When it comes to designing microservices, there are a few key principles to keep in mind:
- Domain-driven design (DDD): This approach involves aligning your services with business capabilities and defining clear boundaries (or "bounded contexts") between them. By organizing your services around business domains, you can ensure that each service is cohesive and focused on a specific task.
- Service communication: With microservices, communication between services is vital. You'll need to decide on the best communication protocols and patterns for your needs, whether it's REST, gRPC, or something else entirely.
- API management: As your microservices architecture grows, managing APIs becomes increasingly important. Amazon API Gateway
can help you create, publish, and secure your APIs, as well as handle tasks like traffic management and monitoring.
- Database strategies: Each microservice should have its own database to ensure loose coupling and independent scalability. This is where the concept of "polyglot persistence" comes in - using different database technologies for different services based on their specific needs.
- Security: AWS offers a range of security features and best practices, from IAM roles and policies to VPCs and security groups.
If you're starting a project from scratch, the next steps are relatively straightforward if you keep these principles in mind. However, you may find yourself facing the daunting task of decomposing an existing monolithic application. This process brings its own unique challenges and involves breaking down the monolith into smaller, more manageable services based on business capabilities or domains.
Decomposing Monoliths
There are several strategies you can employ to tackle this challenge. One approach is to start by identifying seams in the monolith - areas where the application can be logically split based on functionality or data ownership.
Another is to use the strangler pattern, gradually replacing parts of the monolith with microservices over time. Whichever approach you choose, the key is to proceed incrementally, testing and validating each step along the way to ensure a smooth transition.
- Patterns for decomposing monoliths
[AWS Prescriptive Guidance]
Deploying Microservices on AWS
So, assuming that you've designed your microservices architecture (or perhaps decomposed an existing monolith), now it will be time to deploy on AWS. Here are a few options on how you can approach it:
- Containerization with Docker and ECS/EKS: Start by packaging your microservices into Docker containers and deploy them using Amazon ECS or EKS. Docker ensures a consistent and scalable runtime environment, while ECS simplifies scheduling and orchestration through task definitions. Alternatively, EKS provides more control with Kubernetes clusters on AWS.
- Serverless with AWS Lambda: If you prefer a serverless approach, AWS Lambda allows you to run microservices as functions without the need to manage servers. This is particularly beneficial for applications with fluctuating traffic demands, although you should consider factors like cold starts and runtime constraints.
- Serverless Containers with AWS Fargate: For those looking to combine the benefits of serverless computing with containerization, AWS Fargate
offers an efficient solution. Define your services using task definitions similar to ECS, and let AWS handle the underlying infrastructure management, which simplifies deployment processes.
Regardless of your chosen method of deployment, it's important to follow a few key best practices when deploying microservices on AWS, as they ensure efficient resource management, automation, and performance monitoring throughout the deployment process:
- Use AWS CloudFormation
or Terraform for Infrastructure as Code (IaC) to ensure repeatable and controlled resource management.
- Implement a robust CI/CD pipeline to automate builds, tests, and deployments, enhancing efficiency and reliability.
- Employ deployment strategies like blue/green or canary releases to minimize downtime and mitigate risks during updates.
- Monitor performance using AWS CloudWatch
and AWS X-Ray
to gain insights into service behaviour and optimize performance.
With these strategies in place, you'll be well-prepared to deploy your microservices on AWS effectively. Next, let’s delve deeper into integrating CI/CD practices for seamless management and continuous improvement.
Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) is a methodology that plays a vital role in managing microservices on AWS, addressing their complexities and dynamic nature through automated build, test, and deployment processes. This approach ensures services remain deployable, minimizes human error, and speeds up feature delivery.
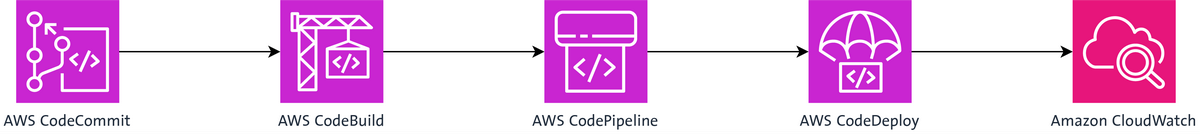
CI/CD pipelines allow for independent updates and scaling of microservices without affecting the entire system, maintaining the agility and flexibility of microservice architectures. AWS offers several tools to facilitate these processes: AWS CodePipeline for defining the release process, AWS CodeBuild
for managing building and testing, and AWS CodeDeploy
for automating deployments to various AWS services like EC2, ECS, and Lambda. Additionally, AWS supports deployment strategies such as Blue/Green deployments and Canary releases to minimize downtime and reduce deployment risks.
Further beneficial practices include monitoring and logging, integral to a robust CI/CD pipeline. AWS provides powerful tools like AWS CloudWatch for collecting and analysing logs, metrics, and events, and AWS X-Ray for tracing requests through the system to pinpoint performance bottlenecks and errors. By making the best use of these CI/CD practices and tools, you can streamline the development process, maintain high availability, and ensure consistent quality across your microservices.

Scaling and Managing Microservices on AWS
As your microservices architecture grows and evolves, you'll need to have strategies in place for scaling and managing your services effectively. AWS provides a range of tools and features to help you keep your services running smoothly, even under heavy load.
- Auto-scaling strategies: Use AWS Auto Scaling
to define scaling policies based on metrics like CPU utilization or request count for efficient resource allocation. Implement Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) to distribute traffic across multiple instances, ensuring high availability and fault tolerance.
- Service discovery and configuration management: Utilize AWS Cloud Map
as a centralized registry to discover and connect to services using logical names instead of hard-coded IP addresses. Securely manage configuration data with AWS Systems Manager Parameter Store
, including database connection strings and API keys.
- Handling failures and implementing resiliency: Implement circuit breakers and retry logic to gracefully handle failures and prevent cascading outages within your microservices architecture. Leverage AWS services such as Amazon Route 53
and Elastic Load Balancing for failover and load balancing across regions and availability zones, ensuring robustness and continuity.
By leveraging these tools and strategies, you can ensure that your microservices architecture is scalable, manageable, and resilient - all while keeping your sanity intact. But don't just take our word for it - let's take a look at a real-world example of microservices in action!
Modernizing ordering systems: A real-world use case

Suppose that, as a furniture manufacturer, you have a traditional ordering system—one that has grown clunky with age. Orders are processed via tightly coupled workflows, every integration is a potential point of failure, and any attempt to scale leads to slowdowns or frustration. What would it look like to modernise that system using AWS and a microservices architecture?
A possible solution might begin by breaking the ordering process into discrete services: order intake, document handling, data storage, fulfilment, and notifications. Each function could then be independently deployed and scaled.
On AWS, this would involve:
- Amazon ECS for containerised services managing workflows like order intake and fulfilment
- Amazon S3
to store order documents, accessible across services
- Amazon DynamoDB
for responsive NoSQL data handling
- Amazon RDS
for relational operations where consistency is critical
To complement the microservices model, serverless services could be introduced to streamline efficiency:
- AWS Lambda
for event-driven triggers like confirming an order or updating status
- Amazon API Gateway to route requests between services and expose them securely to front-end interfaces
This modular approach allows the entire system to scale based on actual usage, improves fault isolation, and reduces deployment overhead. For any manufacturer aiming to simplify operations while improving flexibility and time-to-market, this kind of solution offers a compelling roadmap.
Modernizing ordering systems with the cloud and serverless development
Embracing the Power of Microservices on AWS
In this technical deep-dive, we've highlighted the transformative power of microservices on AWS, emphasizing their scalability, flexibility, and the comprehensive AWS tools that support them. The journey from containerization to serverless computing illustrates how microservices can revolutionize application development.
Above all, it’s important to start small, experiment often, and leverage AWS to unlock the full potential of your applications. With the right approach, you'll build scalable, resilient, and innovative solutions that drive your business forward. Enjoy the exciting and rewarding path to mastering microservices on AWS.
Transform Your App Development with AWS Microservices
Ready to transform your application development with microservices on AWS? Our experts can guide you through the design, deployment and management processes, ensuring your systems are scalable, resilient, and efficient. Contact us and embrace the future of cloud computing with PCG today!
Further Reading
As far as we’ve got in the article, we’ve barely touched upon what is genuinely a vast and intricate topic. Fortunately, AWS offer a wealth of resources to help you take it a step further. Explore these essential guides to enhance your understanding and master the design and deployment of cloud-based microservices on AWS.
- Implementing Microservices on AWS
– An AWS whitepaper providing the definitive guide on the principles and best practices for designing microservices using AWS.
- Let’s Architect! Designing Microservices Architectures
– AWS Architecture Blog post diving deep into architectural considerations for microservices, focusing on service discoverability, connectivity, and asynchronous communication.
- AWS Prescriptive Guidance
– AWS’s prescriptive-guidance PDF on integrating microservices using serverless patterns (API Gateway, decoupled messaging, pub/sub) for modernizing monoliths.

