Application Transformation, Modernization & Refactoring
Modernising software applications is a crucial step for companies to remain competitive. Modernisation means more than just improvement - it's about evaluating and adapting your applications to achieve measurably improved business results.
Our cloud-native approach to your modernisation strategy is based on four strategic steps. First, you need to analyse your current application(s) to define clear goals and KPIs. We then work together to develop a roadmap to implement changes in an orderly sequence and ensure business continuity.
This approach enables you to optimise the scalability, automation and cost savings of the public cloud. Whether lift-and-shift, re-factoring or re-platforming - we guide you through the modernisation process and reconcile quick wins and long-term benefits.
Success Story with LeaseHub
Case Study
LeaseHub: digital game changer for the leasing industry
How LeaseHub is tackling the challenges of the leasing industry and leading the way for innovation and efficiency.
How to modernise your applications in 6 steps
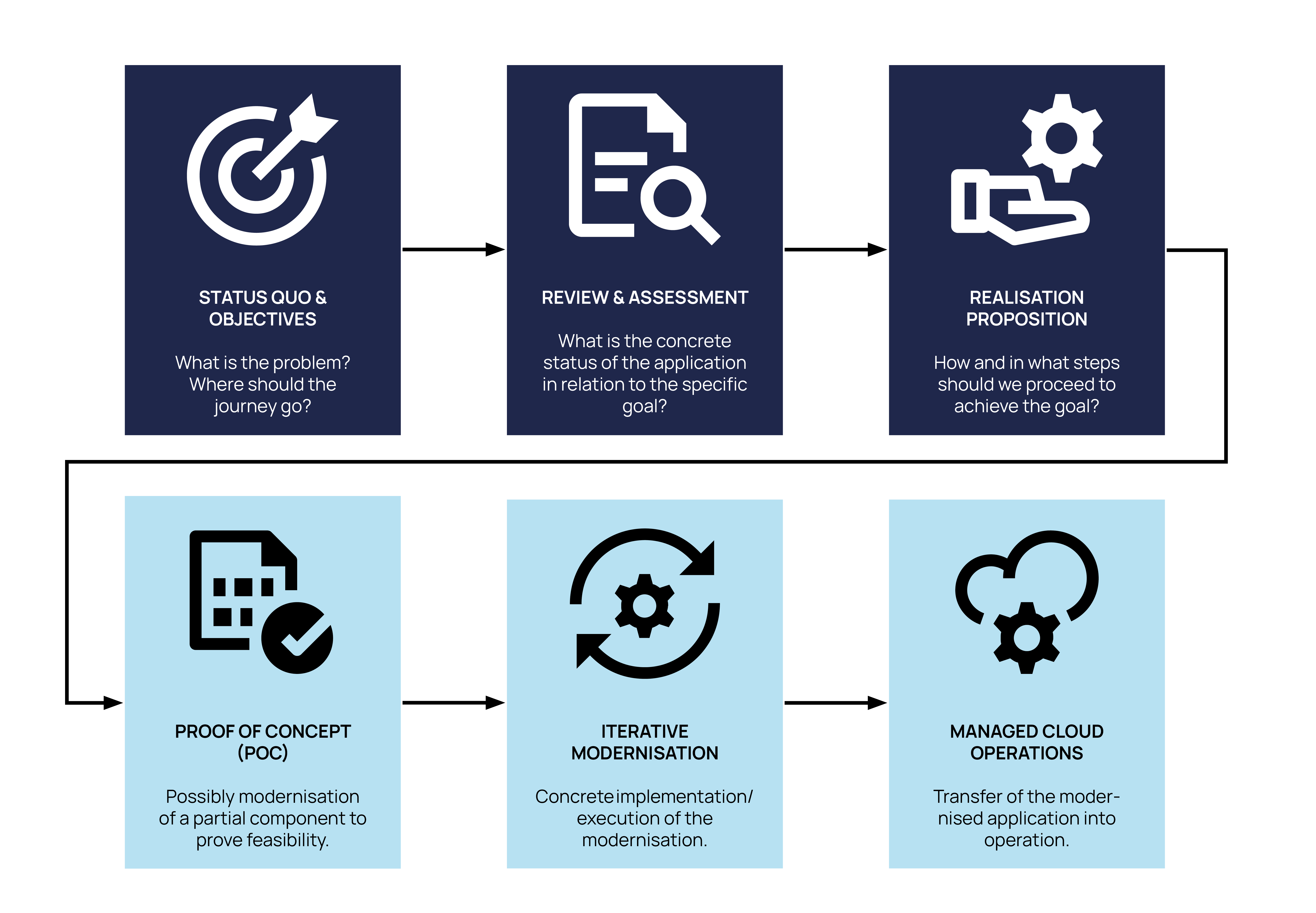
Step 1: Status quo & target vision
The first phase focuses on the current status of the application(s) and the definition of the target vision. Relevant topics are the identification of current pain points with the status quo, the evaluation of the current architecture and the tech stack.
The aim is to gain an understanding of the current state of the application(s) and to develop a clear vision for the desired result. This forms the basis for all further steps of the modernisation journey.
Step 2: Review & assessment
Once the objective has been defined, a review of the application(s) follows. This includes a tool-supported code review, an analysis of the current architecture, a security review and an assessment of the UI/UX. The detailed reviews make it possible to identify the strengths and weaknesses of the application(s) in all relevant facets.
The result is a well-founded analysis of the current status of the application(s), which serves as the basis for optimisation and adaptation to the target vision.
Step 3: Implementation proposal
Following the actual/target analysis, a detailed implementation plan is developed. Various modernisation strategies are presented, quick wins are identified and the procedure is broken down into iterative milestones. The result is a concrete target picture for code, architecture, security and UI/UX and thus an optimal modernisation strategy. The expected operating costs are also taken into account. The result is a comprehensive roadmap that clearly defines all the necessary steps and strategies on the way to the goal.
Step 4: Proof of concept (optional)
A proof of concept (PoC) is useful to validate the feasibility of the planned procedure. This involves modernising a particularly relevant part of the application(s) in order to demonstrate the expected benefits in practice. The PoC shows how the planned measures lead to a reduction in costs and improve performance. This strengthens the stakeholders' confidence in the project and creates a solid basis for further implementation.
The PoC proves the feasibility and demonstrates the benefits of the planned measures.
Step 5: Iterative modernisation
A mixed team setup consisting of internal and external experts (based on the development-team-as-a-service approach) is established. Using an iterative approach, for example with the Strangler Pattern, we modernise the application(s) step by step. Regular releases ensure that improvements can be continuously provided and tested. The transformation of the architecture, the refactoring of the code and the implementation of UI/UX improvements are central components of this phase.
The result is a continuously modernised application that remains available and ready for use throughout the entire process.
Step 6: Managed cloud operations
Once the modernisation is complete, the focus is on the secure and efficient operation of the application(s) in the cloud. A hypercare phase ensures that all functions work as planned and problems are resolved quickly. Continuous uptime monitoring and monitoring of response times ensure high availability. Ongoing modernisation through regular updates and comprehensive security incident monitoring ensure that the application(s) always remain up to date and secure.
By modernising the application and the associated process optimisation, our customer LeaseHub achieved time and cost savings of 46%. Employee satisfaction was increased by 21% and the customer satisfaction rate by as much as 72%.
The advantages of application modernisation

Customised solution approach
For us, there is no one-size-fits-all solution when it comes to modernisation strategy or cloud migration. We help you find the best strategy for your business goals.

Agility and flexibility
More agile and flexible software applications enable organisations to respond faster to changing business needs, deliver new functionality and drive innovation.

Improved performance and scalability
Optimised applications in the cloud ensure better performance as well as scalability. The result is a smoother user experience and more efficient operations.

Cost savings
Cost savings are achieved after modernising the application landscape through reduced resource consumption, lower maintenance costs and more efficient use of infrastructure resources.

Improved security
Security gaps are closed and compliance requirements are better met, resulting in greater security of the IT infrastructure and sensitive company data.

Improved user experience
By modernising software applications, companies can improve the user experience by offering a more user-friendly interface, faster loading times and better integration with other systems.
Choose the cloud-native approach for your modernisation project and use the cloud sustainably.
Read About Our Experience With Application Transformation, Modernization & Refactoring
Case StudyLearn more
From established structures to a future-proof cloud landscape
TB International used PCG to transform its system landscape into a modern, scalable cloud architecture – the basis for innovation, new business models and the rapid connection of external services.
ArticleLearn more
How to successfully migrate VMware workloads to the AWS Cloud
How to successfully bring VMware workloads to AWS: Options, risks and strategies for a future-proof, flexible IT landscape.
ArticleLearn more
Quick wins when modernizing with AWS: What really brings immediate success?
Whether you're planning a project or already using AWS: Discover how AWS can help you quickly save costs, boost resilience, and modernize your IT – without major effort.
ArticleLearn more
Modernisation & cloud transformation with external developer teams
Legacy modernization and cloud transformation with external development teams: risk management, success strategies & best practices
Frequently Asked Questions
What is meant by refactoring software solutions?
The refactoring of software solutions refers to the structured revision of the source code in order to improve readability, maintainability or performance without changing the external behaviour of the software. For example, redundant code fragments are removed, design patterns are applied or inefficient algorithms are optimised in order to increase the quality and reliability of the software. Objective: To increase the maintainability of applications in order to be able to develop them faster and more stably.
When does it make sense for companies to modernise applications in order to move them to the cloud and when should applications be redeveloped?
The decision to modernise an application and migrate it to the cloud or to develop a new one depends on various factors. If an existing application has outdated technologies, is difficult to scale or incurs high maintenance costs, modernisation can make sense in order to improve performance and reduce operating costs. Especially if the application supports critical business processes and a fast time-to-market is required, redevelopment in the cloud may be a better option to take advantage of modern architectures and development practices. Development makes particular sense if an application's programming language is completely outdated, completely new requirements have arisen or the level of technical debt is very high.
In addition, factors such as the complexity of the existing application, availability of resources and budget should also be considered. In some cases, a hybrid strategy may make sense, where certain parts of the application are modernised and migrated to the cloud, while other parts are redeveloped to increase overall efficiency and better achieve business goals. Ultimately, the choice between modernisation and redevelopment is a strategic decision that requires a thorough analysis of requirements, risks and long-term goals.
What advantages do companies have from a well-planned modernisation strategy?
A well-planned modernisation strategy offers companies a wide range of benefits. These include improving the scalability and flexibility of their applications, enabling them to respond quickly to changing market demands. By utilising modern technologies and architectures, companies can increase their competitiveness and provide innovative solutions more quickly. In addition, they can reduce operating costs by implementing more efficient processes and optimising the use of resources. A modernisation strategy also makes it possible to improve security and compliance, as modern cloud platforms often have robust security features. Last but not least, successful modernisation helps to increase customer and employee satisfaction by providing more user-friendly and powerful applications that meet current standards. Ultimately, the time-to-market is shortened as the software can be further developed more efficiently and quickly.
How much time, budget and resources do I need to plan for if I want to implement a modernisation project for my application landscape?
The time, budget and resources required for a modernisation project depend on various factors, including the size and complexity of the existing application landscape, the desired modernisation goals, the available technical skills in the company and the chosen modernisation strategy.