Every week, we have the pleasure of talking with CxOs and Security Leaders about their security compliance, especially focusing on the gold standard ISO 27001. This guide is designed to help you understand the framework better and get your implementation started.
Introduction to ISO 27001
What is ISO 27001 and Why It Matters in 2025
ISO 27001 Compliance is a comprehensive international framework that guides organizations in managing, monitoring, reviewing, implementing, and maintaining their information security. It enables organizations to ensure the confidentiality, availability, and integrity of their information security management system (ISMS).
ISO 27001 is a part of the broader 27000 family of standards that collectively offer informationsecurity best practices for organizations of all types and sizes. It facilitates holistic infosec management of a wide range of data.
The Significance of ISO 27001 in Today's World
Implementing ISO 27001 helps organizations protect against data breaches, cyber-attacks, and theft or loss of data, ensuring business continuity and resilience.
Why ISO 27001 is Globally Recognized and its Benefits
The global recognition of ISO 27001 comes from its ability to be applied in any organization, regardless of size or industry. Here are the biggest benefits of ISO 27001:
1. Protection Against Security Threats: Guards organizations against both external cyber threats and internal errors.
2. Regulatory Compliance: Helps in adhering to laws like GDPR and other data protection mandates, thereby avoiding fines.
3. Reputation Management: Demonstrates a firm's commitment to information security to stakeholders, enhancing its reputation.
4. Improved Structure and Focus: Mandates annual risk assessments, fostering better organizational structure and focus.
5. Reduced Audit Frequency: ISO 27001 certification is globally recognized, reducing the need for frequent audits.
6. Competitive Advantage: Adopting ISO 27001 can set a company apart from its competitors, showcasing a commitment to secure and reliable operations.
7. Sales Accelerator: Certification can act as a trust signal to potential clients, potentially speeding up sales processes.
8. Assurance for Customers: Provides customers with the confidence that their data is managed securely and responsibly.
9. Mandatory for Cybersecurity Insurances: Increasingly required for obtaining cybersecurity insurance, as it indicates a robust approach to managing information security risks.
ISO 27001's comprehensive approach to information security management makes it a valuable asset for organizations looking to enhance their security posture and business operations.
Breaking Down ISO 27001:2022 - Components and Structure
ISO 27001:2022 has undergone notable revisions, especially in Annex A, which deals with security controls. Here are the key changes:
Reduction in the Number of Controls: The total number of controls in ISO 27001:2022 has decreased from 114 to 93. This reduction is mainly due to the merging of multiple controls.
Restructuring of Control Categories: Instead of the previous 14 categories, the controls are now organized into 4 sections:
A.5 Organizational Controls: This section encompasses 37 controls and focuses on the broader organizational framework for information security.
A.6 People Controls: Contains 8 controls, emphasizing the role of human resources in information security.
A.7 Physical Controls: Comprises 14 controls, dealing with the physical aspects of information security.
A.8 Technological Controls: This section, with 34 controls, addresses the technological aspects of securing information.
Introduction of New Controls: There are 11 new controls in ISO 27001:2022, reflecting the evolving trends in IT and security:
- Threat Intelligence
- Information Security for the Use of Cloud Services
- ICT Readiness for Business Continuity
- Physical Security Monitoring
- Configuration Management
- Information Deletion
- Data Masking
- Data Leakage Prevention
- Monitoring Activities
- Web Filtering
- Secure Coding
Changes in Main Clauses: The main part of ISO 27001, clauses 4 to 10, has seen slight modifications, such as the addition of requirements for planning processes and their interactions in the ISMS, and emphasis on internal communication of roles within the organization.
Title Changes and Control Mergers: Of the existing controls, 35 have remained the same, 23 have been renamed, and 57 have been merged into 24 controls.
These changes reflect a more streamlined approach to organizing information security controls and adapting to the latest trends in technology and security. The revision aims to make the standard more applicable and effective in today's fast-evolving digital landscape
ISO 27001 Certification Step-by-step
The ISO 27001 implementation can be broken down into eight steps:
1. Planning: Efficient planning is crucial for the smooth execution of the certification process.
2. Defining ISMS: The foundation of the certification process, tailored to your organization.
3. Risk assessment: Identifying and evaluating information security risks.
4. Policies and control: Developing policies and controls to manage identified risks.
5. Employee training: Training staff to execute policies properly.
6. Documentation: Keeping thorough records of all processes for audit purposes.
7. Internal and external audits: Performing audits to identify and rectify deviations before certification.
8. Continuous periodic audits: Regularly reviewing and improving the ISMS to address new threats.
Timeline and Resources Needed
The process typically spans 3 to 12 months, depending on your company's existing security practices, maturity, and size.
Risk Management in ISO 27001
The Role of Risk Assessment
Risk assessment is a critical component of the ISO 27001 ISMS, enabling organizations to identify, analyze, and address information security risks.
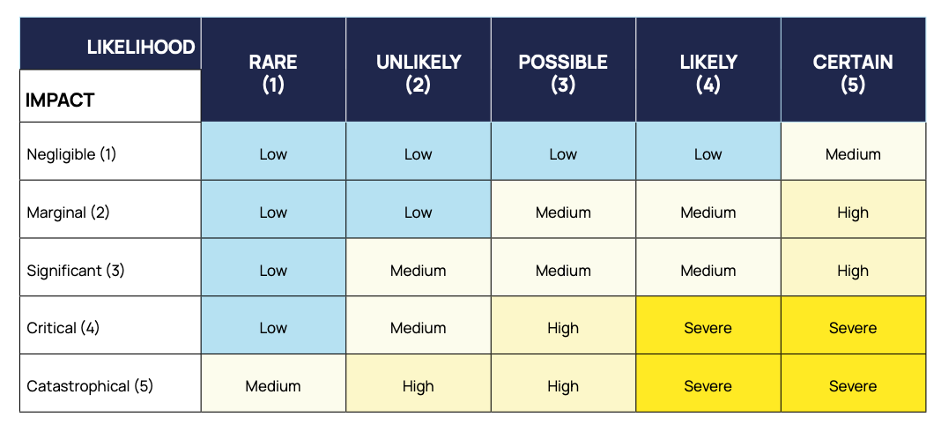
Most risk assessment matrices are designed with one axis representing the probability of a risk scenario occurring and the other representing the potential damage it will cause. In the center, scores are assigned based on the combined totals of probability and impact.
You should use the matrix to score each risk and compare the totals against your predetermined levels of acceptable risk (i.e., your risk appetite). These scores will guide how you address each risk, which is the final step in the process.
5 Steps for Effective Risk Management
1. Establish a risk management framework: This sets the conditions for performing a risk assessment.
2. Identify risks: The most time-consuming part where you identify risks that can affect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information.
3. Analyse risks: Identify the threats and vulnerabilities that apply to each asset.
4. Evaluate risks: Assess how significant each risk is and prioritize them.
5. Treat risks: Determine how to address each risk, whether through avoidance, mitigation, or acceptance.
Documenting Your ISO 27001 Compliance
Key Documents and Record-Keeping
Organizations must complete appropriate documents to demonstrate compliance with ISO 27001. The mandatory documents include:
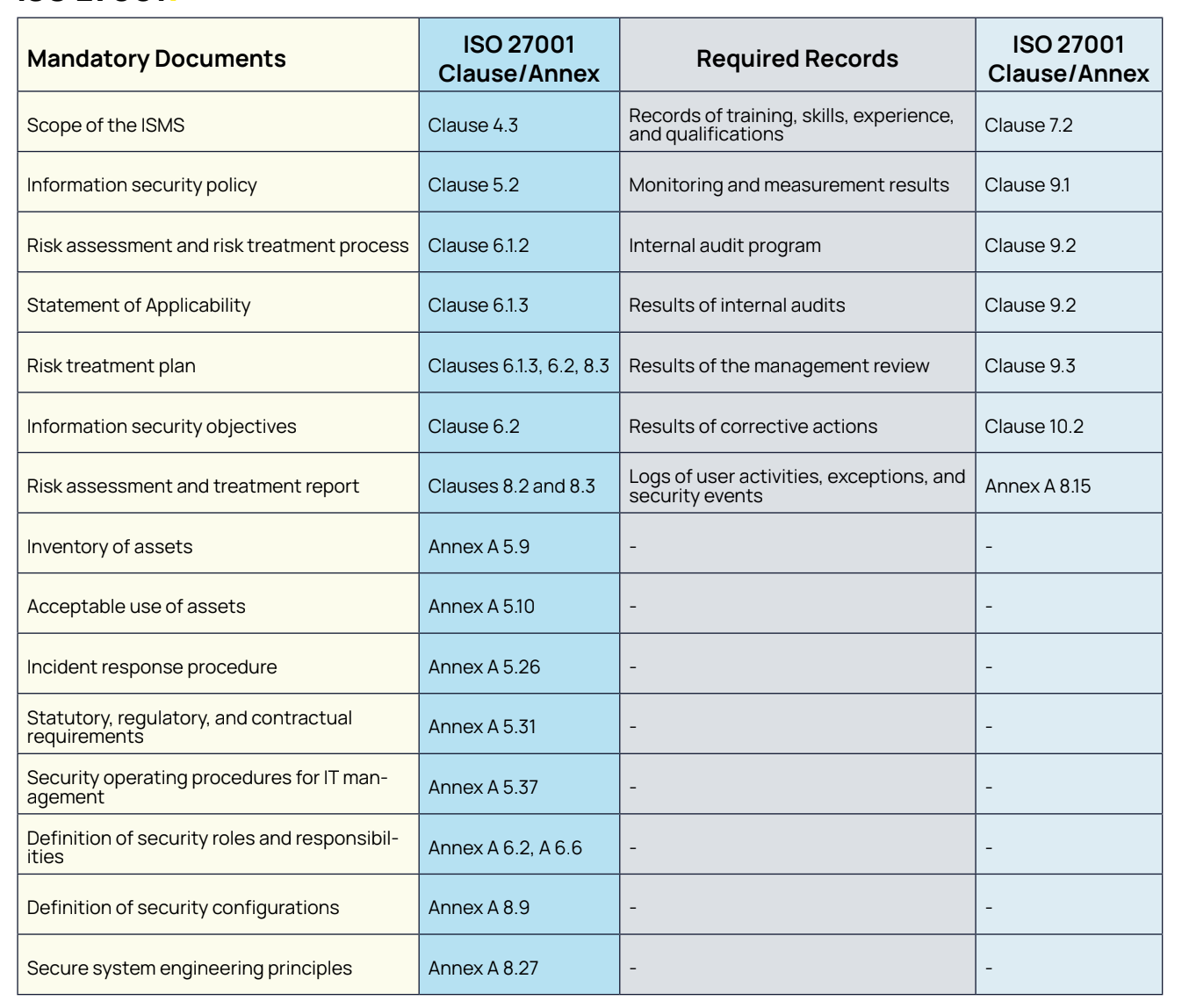
This update aligns with the ISO 27001: 2022 version. This recent version requires fewer documents compared to the ISO 27001: 2013 version. There are no extra documents needed for the 11 new controls introduced in the latest update.
Additionally, while there are several non-mandatory documents that can aid in the implementation of the ISO standard, they aren’t explicitly deemed essential. However, auditors often review these documents to ensure that an organization’s ISMS is robust, well-established, and that risks are effectively managed. These documents encompass:
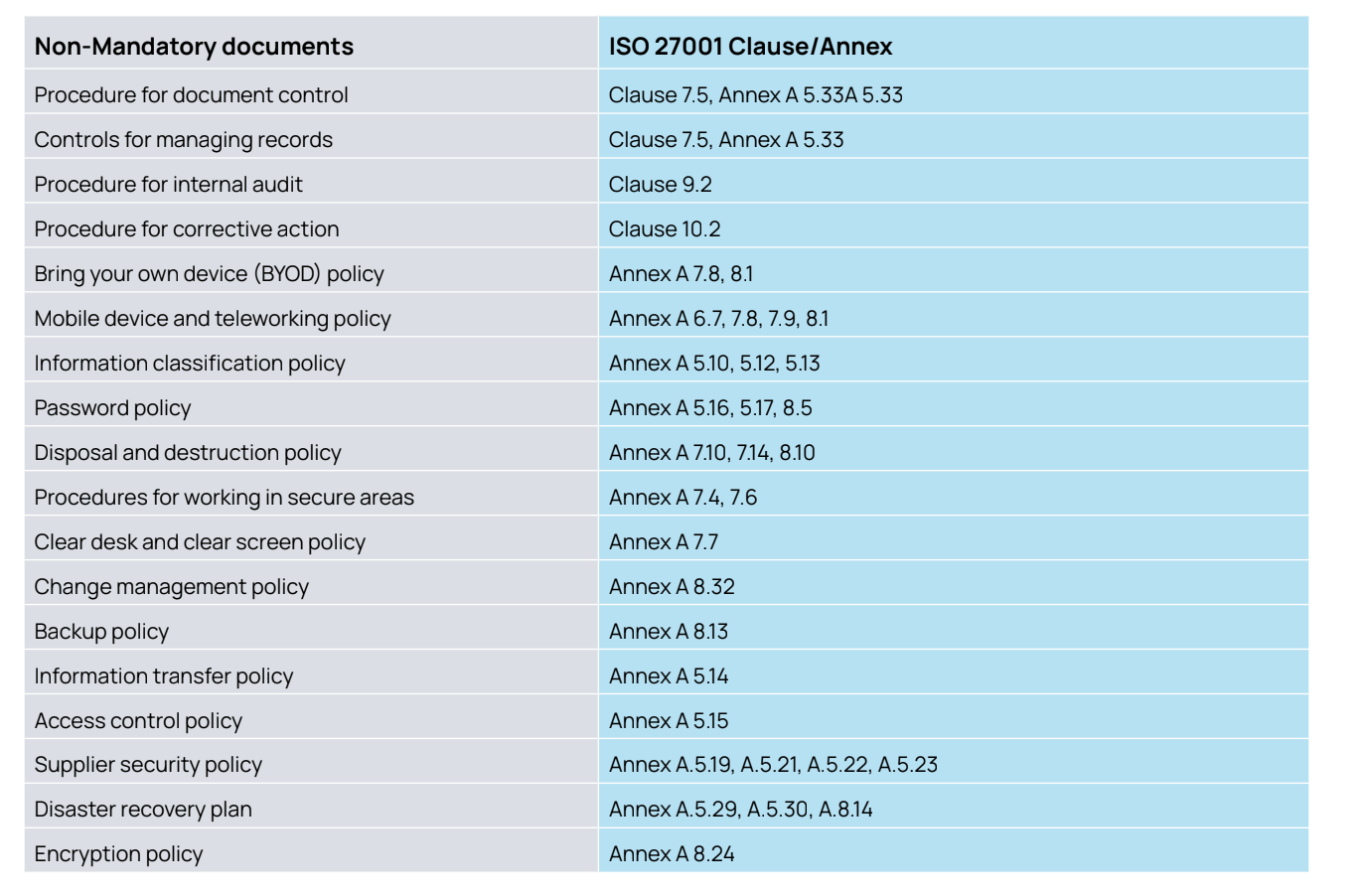
Best Practices in Documentation
Documenting ISO 27001 compliance can be a complex and daunting task due to the extensive number of policies required and limited guidance provided by the standard itself. Organizations typically adopt one of three strategies:
- Trial and Error: Not recommended due to potential high costs and lack of strategic planning.
- Hiring Consultants: More expensive but safer and faster for achieving compliance.
- Purchasing a Documentation Toolkit: Provides templates and tools that help meet the standards' requirements.
Monitoring and Review Strategies
Clause 9.1 of ISO 27001 requires organizations to assess the performance and effectiveness of their Information Security Management System (ISMS). When seeking ISO 27001 certification, auditors will examine several key areas:
- The specific elements the organization has chosen to monitor and measure, encompassing not only the objectives but also the associated processes and controls.
- The strategies the organization will employ to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the results from their measurement, monitoring, analysis, and evaluation activities.
- The timing and frequency of these activities, as well as the identification of the personnel responsible for carrying them out.
- The manner in which the organization utilizes the results obtained from these activities.
Accurate and comprehensive documentation is critical in ISO 27001—organizations must be able to describe their monitoring and measurement strategies and demonstrate that these activities are being conducted effectively as a key to successful certification.
Training and Staff Competence in ISO 27001
One of the key requirements of ISO 27001 is that organizations must ensure that the people who work on the ISMS are competent. This means that they must possess the necessary knowledge, skills, and experience to perform their roles effectively.
Clause 7.2 of ISO 27001 addresses the competence of personnel. This clause requires organizations to determine the necessary competence levels for individuals performing activities that affect the ISMS, including:
- Determine the necessary competence of person(s) doing work under its control that affects its information security performance.
- Ensure that these persons are competent based on appropriate education, training, or experience.
- Where applicable, take action to acquire the necessary competence and evaluate the effectiveness of these actions.
- Retain appropriate documented information as evidence of competence.
The Internal Audit: Ensuring Continuous Improvement
An ISO 27001 internal audit entails a detailed review of your organization's ISMS to ascertain its compliance with the standard's requirements. This audit, distinct from a certification review, is carried out by either your staff or external consultants. The findings are utilized to direct the future development of your ISMS. The criteria for conducting an internal audit are specified in Clause 9.2 of ISO 27001. The requirement here ist that you can demonstrate the planning requirements, the planned audit frequency and timing, the methods for conducting the audit, the assignment of responsibilities, and reporting.
Integrating ISO 27001 with Other Standards
The standard can be integrated with other management system standards, providing a cohesive approach to organizational governance. Standards that are combined with Iso 27001 are usually ISO 9001, SOC 2 or TISAX.
Leveraging Technology for ISO 27001 Compliance
An ISO 27001 compliance automation solution helps you kickstart the process of getting your organization certification-ready at any stage. It not only eliminates the complexities associated with manual certification but also accelerates the process by automating evidence collection, providing comprehensive expertise, and enabling continuous monitoring. This results in more intelligent workflows, streamlined policy implementation, and faster certification at a reduced cost.
Frequently Asked Questions About ISO 27001
Is ISO 27001 mandatory?
Any business or service provider that handles, manages, or transmits client data should comply with ISO 27001. While it is not mandatory, operating without a robust security framework is becoming increasingly difficult.
How does ISO 27001 affect internal processes and operations?
ISO 27001 promotes a proactive security mindset, leading to the development of mature and efficient internal processes. It emphasizes continuous improvement and risk management, enhancing operational maturity and streamlining workflows.
When will ISO 27001 be updated?
The International Accreditation Forum (IAF) has released a document indicating that, starting from the publication of ISO 27001:2022, certified organizations have 36 months to complete the transition, which in this case is no later than October 31, 2025.
What is the difference between ISO 27001 and ISO 27002?
ISO 27002 is a supplementary standard that provides guidance on implementing the security controls listed in Annex A of ISO 27001. ISO 27001 is the one organizations typically certify to. However, once the controls for implementation are identified, ISO 27002 can be consulted to understand the workings of each control.
ISO 27001 vs. SOC 2?
The main difference between SOC 2 and ISO 27001 is that SOC 2 is focused on demonstrating security controls that protect customer data, while ISO 27001 requires evidence of an operational ISMS for managing InfoSec continuously. SOC 2 is prevalent in the United States, whereas ISO 27001 is widely accepted in European countries.
ISO 27001 vs. Cyber Essentials?
Cyber Essentials is more cost-effective and serves as a good initial step for small and medium-sized enterprises to foster a security-minded culture. However, its recognition is primarily within the UK. UK Government suppliers are required to achieve Cyber Essentials as part of their contractual obligations.
What are the costs associated with ISO 27001?
The costs for ISO 27001 certification can vary, with factors such as company size and certification scope affecting the total. For small and medium-sized businesses, the cost usually ranges from €10,000 to €50,000.
Is there an ISO 27001 “fast-track”?
ISO 27001 isn't just a checkbox exercise. You don't need to start by building Fort Knox, but neglecting the ISMS after initial certification will lead to failure in future audits and won't provide any value to the organization. However, with a combination of external expertise, audit coaching, and automation tooling, you will be able to achieve certification much faster than with a classical approach.
How We Can Help You
With PCG, you benefit from over 10 years of experience in implementing security compliance. Reach out for a free consultation and get a detailed roadmap for implementing ISO 27001 in your organization.