"Hyperscalers" in the public cloud sector are international cloud providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure or Google. They provide the basic components of a public cloud, consisting of virtual resources such as computing power, storage and network, via a freely accessible platform.
The hyperscalers are pursuing a clear objective with their public cloud offerings:
- Scalability: Each customer can scale up or down their own public cloud environment to the appropriate size.
- Agility: Hyperscalers' public cloud resources and services are available to customers in real time via one platform. Starting up various services only takes a few minutes. The public cloud environment is therefore quickly efficient.
- Cost transparency: Hyperscalers work according to the "pay-per-use" principle, which means that customers only pay for the public cloud resources they actually use
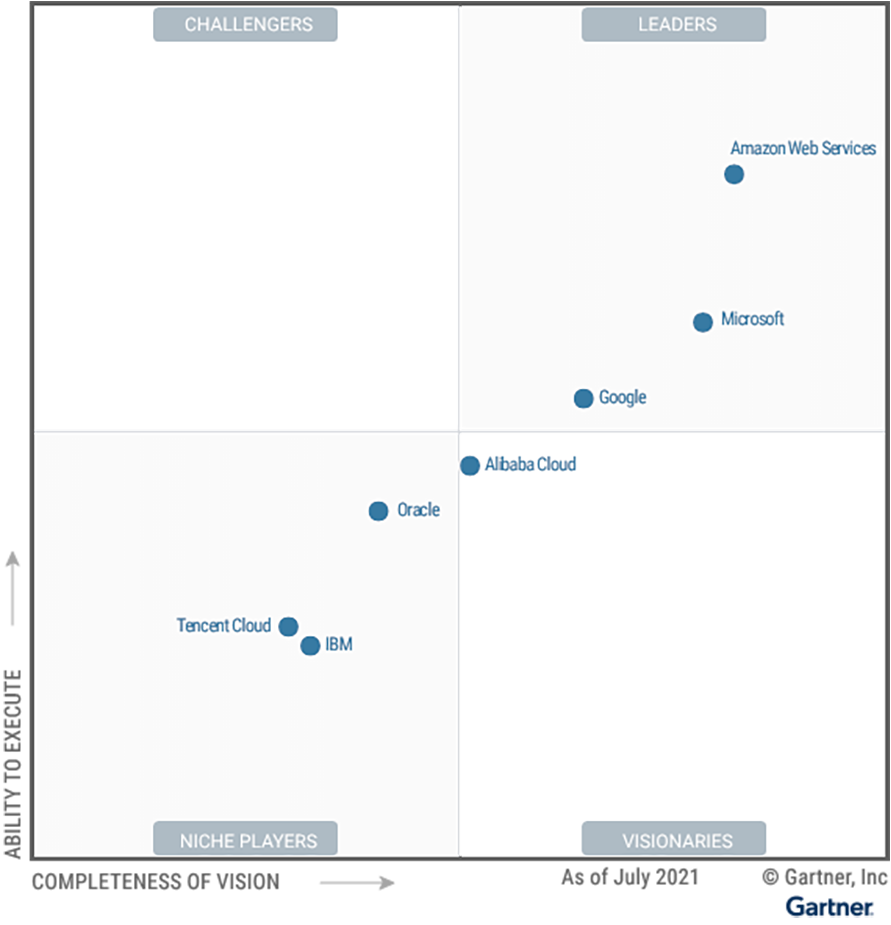
Once a year, the consulting firm Gartner honours the leading public cloud providers in their "Magic Quadrant™ for Cloud Infrastructure and Platform Services". The "leaders" among the hyperscalers in the review include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud.

Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is the market leader in the field of public cloud platforms. Emerging from the international retail group Amazon, AWS was founded in 2008. This makes it the cloud platform that has been on the market for the longest time compared to the other hyperscalers and, with over 200 services, has the largest range for customers of all industries and sizes.

Microsoft Azure
Microsoft Azure is the cloud platform from Microsoft. It offers the basic resources of a public cloud platform, including compute, storage and networking. Initially designed for development, Microsoft Azure has been available to the public since October 1, 2010 under the name "Windows Azure''. The hyperscaler was officially relaunched as Microsoft Azure in April 2014, and since then has been consistently enhanced with additional services.

Google Cloud
The Google Cloud Platform is a suite of public cloud services that includes various tools and a range of modular offerings such as computing, storage, analytics, and machine learning. Google's public cloud offering became generally available in November 2011, marking the start of its ascent as a hyperscaler in the cloud infrastructure sector.